Buying 200-301 Dumps Questions (2024): A Critical Decision for Cisco 200-301 CCNA Exam PreparationBuying 200-301 Dumps Questions (2024): A Critical Decision for Cisco 200-301 CCNA Exam Preparation

While preparing for the 200-301 exam, you need to make a crucial decision: choose the right study material, and the 200-301 dumps questions (2024) are the best option to prepare for the exam.
To ensure your success in the Cisco 200-301 CCNA exam, it is crucial to purchase the 200-301 dumps questions (2024) for PassitSure updates.
Buy 200-301 dumps questions (2024) links: https://www.pass4itsure.com/200-301.html (Optional PDF or VCE format) All of these dumps questions and answers provide accurate and up-to-date information consistent with the exam syllabus, rest assured.
What’s new in Cisco CCNA certification 2024
Over the years, Cisco has been looking for changes to keep up with the market.
In 2022 and 2024, Cisco made a complete change to its certification process, eliminating many areas of expertise such as Cisco CCNA voice and security, and controversially molding some CCIE courses, resulting in many experts in areas such as voice and collaboration no longer being certified!
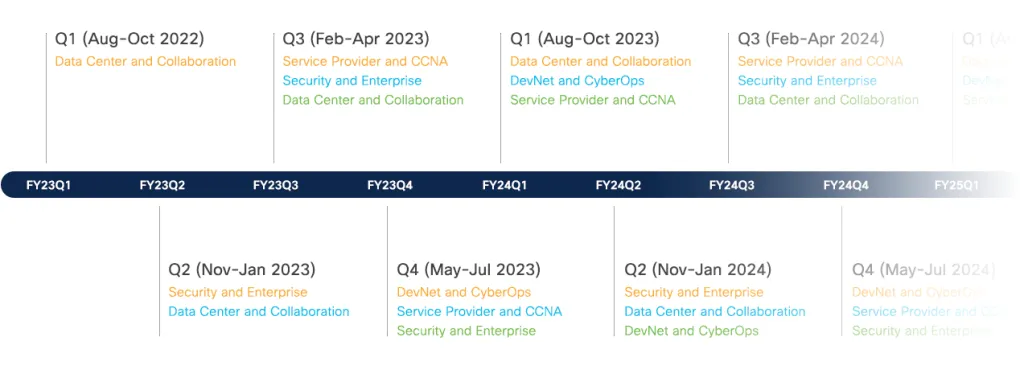
Reading the chart entries for service providers and CCNAs, you’ll see that as of today (April 15, 2024), there aren’t any announcements yet, and the bottom tab of the CCNA shows that nothing will change this year, so you can safely assume it will remain as it is until the end of 2024.
You can try here first, free Cisco 200-301 CCNA exam questions, practice below.
Free 200-301 dumps questions shared online Q16-Q30:
The Cisco CCNA (200-301) exam is 120 minutes long and consists of 100-120 questions. Questions can be multiple-choice, drag-and-drop, mock, and other types.
Pick up where you shared last time (200-301 exam questions Q1-Q15) and share 15 more latest exam questions (total questions 1450)
Question 16:
A network engineer is configuring a switch so that it is remotely reachable via SSH. The engineer has already configured the hostname on the router. Which additional command must the engineer configure before entering the command to generate the RSA key?
A. password Password
B. crypto key generates rsa modulus 1024
C. ip domain-name domain
D. ip ssh authentication-retries 2
Correct Answer: C
Question 17:
Which command must be entered so that the default gateway is automatically distributed when DHCP is configured on a router?
A. DNS-server
B. default-router
C. ip helper-address
D. default-gateway
Correct Answer: B
Question 18:
Why is a first-hop redundancy protocol implemented?
A. to enable multiple switches to operate as a single unit
B. to provide load-sharing for a multilink segment
C. to prevent loops in a network
D. to protect against default gateway failures
Correct Answer: D
Question 19:
DRAG DROP
Drag and drop the IPv4 network subnets from the left onto the correct usable host ranges on the right.
Select and Place:
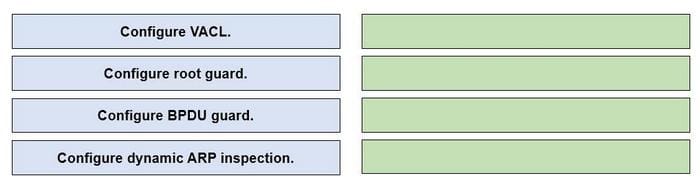
Correct Answer:

This subnet question requires us to grasp how to subnet very well. To quickly find out the subnet range, we have to find out the increment and the network address of each subnet. Let\’s take an example with the subnet 172.28.228.144/18:
From the /18 (= 1100 0000 in the 3rd octet), we find out the increment is 64. Therefore the network address of this subnet must be the greatest multiple of the increment but not greater than the value in the 3rd octet (228).
We can find out the 3rd octet of the network address is 192 (because 192 = 64 * 3 and 192 < 228) -> The network address is 172.28.192.0. So the first usable host should be 172.28.192.1 and it matches with the 5th answer on the right. In this case, we don’t need to calculate the broadcast address because we found the correct answer.
Let\’s take another example with subnet 172.28.228.144/23 -> The increment is 2 (as /23 = 1111 1110 in 3rd octet) -> The 3rd octet of the network address is 228 (because 228 is the multiply of 2 and equal to the 3rd octet) -> The network address is 172.28.228.0 -> The first usable host is 172.28.228.1. It is not necessary but if we want to find out the broadcast address of this subnet, we can find out the next network address, which is 172.28. (228 + the increment number).0 or
172.28.230.0 then reduce 1 bit -> 172.28.229.255 is the broadcast address of our subnet. Therefore the last usable host is 172.28.229.254.
Question 20:
What is the expected outcome when network management automation is deployed?
A. A distributed management plane must be used.
B. Software upgrades are performed from a central controller
C. Complexity increases when new device configurations are added
D. Custom applications are needed to configure network devices
Correct Answer: B
Question 21:
Which two IPv6 addresses are used to provide connectivity between two routers on a shared link? (Choose two)
A. FF02::0001:FF00:0000/104
B. ff06:bb43:cc13:dd16:1bb:ff14:7545:234d
C. 2002::512:1204b:1111::1/64
D. 2001:701:104b:1111::1/64
E. ::ffff:10.14.101.1/96
Correct Answer: DE
the IPv6 address “::ffff:10.14.101.1/96” is a valid representation of an IPv6 address with an embedded IPv4 address. This format is known as an IPv4-mapped IPv6 address.
In this case, “::ffff:10.14.101.1” represents the IPv4 address “10.14.101.1” embedded within an IPv6 address. The “::ffff:” prefix indicates that the following part of the address is an IPv4 address. The “/96” suffix indicates the network prefix length, specifying that the first 96 bits represent the network portion of the address.
Question 22:
What is a DHCP client?
A. a workstation that requests a domain name associated with its IP address
B. a host that is configured to request an IP address automatically
C. a server that dynamically assigns IP addresses to hosts.
D. a router that statically assigns IP addresses to hosts.
Correct Answer: B
Question 23:
Refer to the exhibit. A network associate has configured OSPF with the command:
City(config-router)# network 192.168.12.64 0.0.0.63 area 0
After completing the configuration, the associate discovers that not all the interfaces are participating in OSPF. Which three of the interfaces shown in the exhibit will participate in OSPF according to this configuration statement? (Choose three.)

A. FastEthernet0 /0
B. FastEthernet0 /1
C. Serial0/0
D. Serial0/1.102
E. Serial0/1.103
F. Serial0/1.104
Correct Answer: BCD
The “network 192.168.12.64 0.0.0.63 equals to network 192.168.12.64/26. This network has:
1.
Increment: 64 (/26= 1111 1111.1111 1111.1111 1111.1100 0000) + Network address:192.168.12.64
2.
Broadcast address: 192.168.12.127
Therefore all interfaces in the range of this network will join OSPF.
Question 24:
The service password-encryption command is entered on a router. What is the effect of this configuration?
A. restricts unauthorized users from viewing clear-text passwords in the running configuration
B. prevents network administrators from configuring clear-text passwords
C. protects the VLAN database from unauthorized PC connections on the switch
D. encrypts the password exchange when a VPN tunnel is established
Correct Answer: A
Question 25:
Refer to the exhibit.

All interfaces are configured with duplex auto and IP OSPF network broadcast. Which configuration allows routers R14 and R86 to form an OSPFv2 adjacency and act as a central point for exchanging OSPF information between routers?
A. R14# interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 10.73.65.65 255.255.255.252 ip ospf priority 255 ip mtu 1500 router ospf 10 router-id 10.10.1.14 network 10.10.1.14 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 10.73.65.64 0.0.0.3 area 0
R86#
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 10.73.65.66 255.255.255.252
ip mtu 1400
router ospf 10
router-id 10.10.1.86
network 10.10.1.86 0.0.0.0 area 0
network 10.73.65.64 0.0.0.3 area 0
B. R14# interface Loopback0 ip ospf 10 area 0 interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 10.73.65.65 255.255.255.252 ip ospf 10 area 0 ip mtu 1500 router ospf 10 ip ospf priority 255 router-id 10.10.1.14
R86#
interface Loopback0
ip ospf 10 area 0
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 10.73.65.66 255.255.255.252
ip ospf 10 area 0
ip mtu 1500
router ospf 10 router-id 10.10.1.86
C. R14# interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 10.73.65.65 255.255.255.252 ip ospf priority 0 ip mtu 1500 router ospf 10 router-id 10.10.1.14 network 10.10.1.14 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 10.73.65.64 0.0.0.3 area 0
R86#
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 10.73.65.66 255.255.255.252
ip mtu 1500
router ospf 10
router-id 10.10.1.86
network 10.10.1.86 0.0.0.0 area 0
network 10.73.65.64 0.0.0.3 area 0
D. R14# interface Loopback0 ip ospf 10 area 0 interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 10.73.65.65 255.255.255.252
ip ospf priority 255
ip ospf 10 area 0
ip mtu 1500
router ospf 10
router-id 10.10.1.14
R86#
interface Loopback0
ip ospf 10 area 0
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 10.73.65.66 255.255.255.252
ip ospf 10 area 0
ip mtu 1500
router ospf 10
router-id 10.10.1.86
Correct Answer: D
A router with “priority 0” and another with “priority default (1)” formed adjacency and exchanged LSAs and LSDBs normally (I tested it in P.Trace and OSPF dynamic routing works normally), the difference is that there will not be a DR Backup in case fail (that\’s all). One will be DR Other (neighbor Full/DR) and one DR (neighbor Full/DROther), and BDR appears written that it does not exist because priority 0 cannot be either DR or BDR.
(Observation: “point-to-point type” is recommended for this type of connection.)
However, the exercise asks them to act as a central point for exchanging information, in this case, “it gives the impression” that he asked us to select a “DR”. Letter “D” would be the most correct because using “ip ospf priority 255” (in the interface) we define R14 as DR.
Question 26:
Refer to the exhibit.
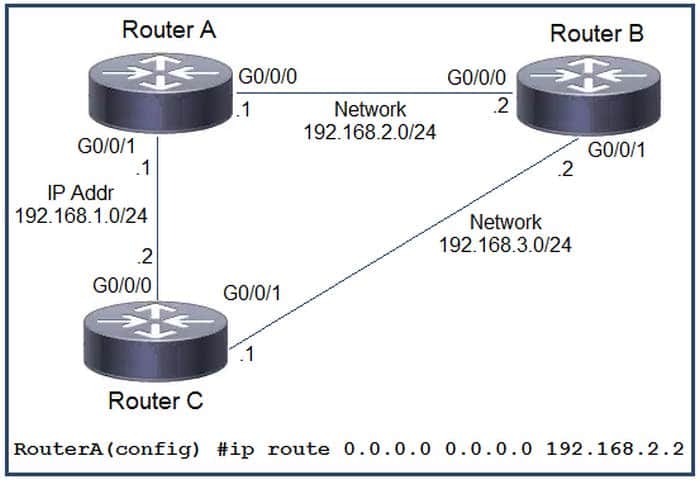
Which command must be issued to enable a floating static default route on router A?
A. lp route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.2
B. ip default-gateway 192.168.2.1
C. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.2.1 10
D. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.2 10
Correct Answer: D
Question 27:
Refer to the exhibit.
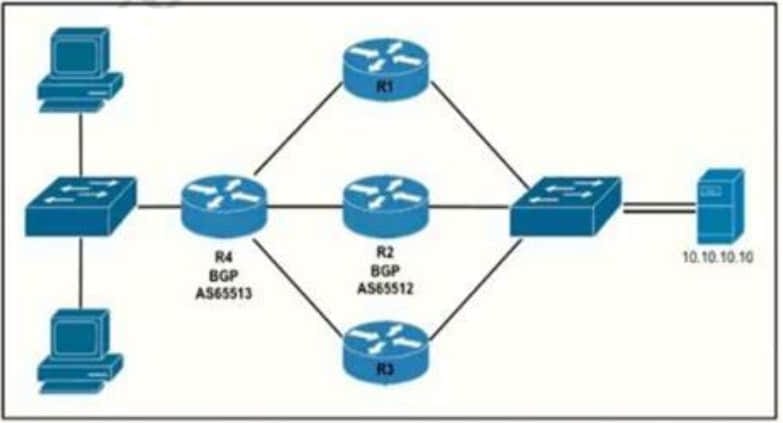
Router R4 is dynamically learning the path to the server. If R4 is connected to R1 via OSPF Area 20, to R2 via R2 BGP, and to R3 via EIGRP 777, which path is installed in the routing table of R4?
A. the path through R1, because the OSPF administrative distance is 110
B. the path through R2. because the IBGP administrative distance is 200
C. the path through R2 because the EBGP administrative distance is 20
D. the path through R3. because the EIGRP administrative distance is lower than OSPF and BGP
Correct Answer: C
Question 28:
In QoS, which prioritization method is appropriate for interactive voice and video?
A. traffic policing
B. round-robin scheduling
C. low-latency queuing
D. expedited forwarding
Correct Answer: D
Question 29:
Which two actions are performed by the Weighted Random Early Detection mechanism? (Choose two.)
A. It supports protocol discovery.
B. It guarantees the delivery of high-priority packets.
C. It can identify different flows with a high level of granularity.
D. It can mitigate congestion by preventing the queue from filling up.
E. It drops lower-priority packets before it drops higher-priority packets.
Correct Answer: DE
Weighted Random Early Detection (WRED) is just a congestion avoidance mechanism. WRED drops packets selectively based on IP precedence. Edge routers assign IP precedences to packets as they enter the network. When a packet arrives, the following events occur:
1. The average queue size is calculated.
2. If the average is less than the minimum queue threshold, the arriving packet is queued.
3. If the average is between the minimum queue threshold for that type of traffic and the maximum threshold for the interface, the packet is either dropped or queued, depending on the packet drop probability for that type of traffic.
4. If the average queue size is greater than the maximum threshold, the packet is dropped.
WRED reduces the chances of tail drop (when the queue is full, the packet is dropped) by selectively dropping packets when the output interface begins to show signs of congestion (thus it can mitigate congestion by preventing the queue from filling up).
By dropping some packets early rather than waiting until the queue is full, WRED avoids dropping large numbers of packets at once and minimizes the chances of global synchronization. Thus, WRED allows the transmission line to be used fully at all times.
WRED generally drops packets selectively based on IP precedence. Packets with a higher IP precedence are less likely to be dropped than packets with a lower precedence. Thus, the higher the priority of a packet, the higher the probability that the packet will be delivered
Question 30:
Refer to the exhibit. The DHCP server and clients are connected to the same switch. What is the next step to complete the DHCP configuration to allow clients on VLAN 1 to receive addresses from the DHCP server?
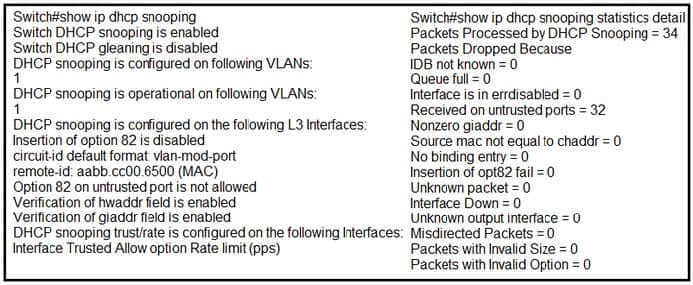
A. Configure the ip dhcp snooping trust command on the interface that is connected to the DHCP client.
B. Configure the ip dhcp relay information option command on the interface that is connected to the DHCP client.
C. Configure the ip dhcp snooping trust command on the interface that is connected to the DHCP server.
D. Configure the Ip dhcp relay information option command on the interface that is connected to the DHCP server.
Correct Answer: C
If a Layer 2 LAN port is connected to a DHCP server, configure the port as trusted by entering the ip dhcp snooping trust interface configuration command. https://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/Test/dwerblo/broken_guide/snoodhcp.html#wp1073367
In addition to the help of the 200-301 dumps, you will need Cisco official training to prepare for your certification exam to pass the exam or take advantage of the self-study resources on the Cisco Learning Network for self-study.
This prepares you for a new collection of 200-301 learning resources (with links):
Document:
Books:
- CCNA 200-301 Official Cert Guide, Volume 2
- Ccna certification study guide, volume 2: Exam 200-301
- CCNA
- CCNA Preparation Library (640-801) by Stephen McQuerry
- Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) Study Guide (640-802) by Todd Lammle
Videos:
- CCNA Certification Training Videos
- CCNA Prep Program Webinars
- CCNA Prep Program – Learning Map
- CCNA Prep Program Practice Quiz
Of course, there are many more good study materials, and I have listed here only what I think is good, and others are welcome to add.
Still a little confused, about the 200-301 exam.
How is the CCNA 200-301 exam difficult and how do I prepare?
It’s a little difficult, but with the right approach, it’s easy. Passing the CCNA 200-301 exam, the world’s most famous exam, requires practice, consistent effort, and dedication. Also, have proper study material –200-301 dumps questions(Pass4itSure).
Does someone say that CCNP is harder than CCNA? Is this correct?
Yes, the CCNA exam is easier than the CCNP exam. One of the reasons why the CCNA exam is considered easier is that it covers a smaller range of topics than the CCNP exam.
Do I have to take more practice exercises to pass the Cisco CCNA (200-301) exam?
Yes, trying mock exams is a smart way to change the way you study and ensure that you do well on the actual exam. When you practice, it helps you identify weak points and strengthen them.
Conclusion:
With the purchase of 200-301 dumps questions (2024), you can confidently prepare for the Cisco 200-301 CCNA exam which guarantees that you are learning the right content and increases your chances of success.
So, go for it. Download the new 200-301 dumps 2024 new questions https://www.pass4itsure.com/200-301.html (PDF or VCE format) to start proper exam preparation.